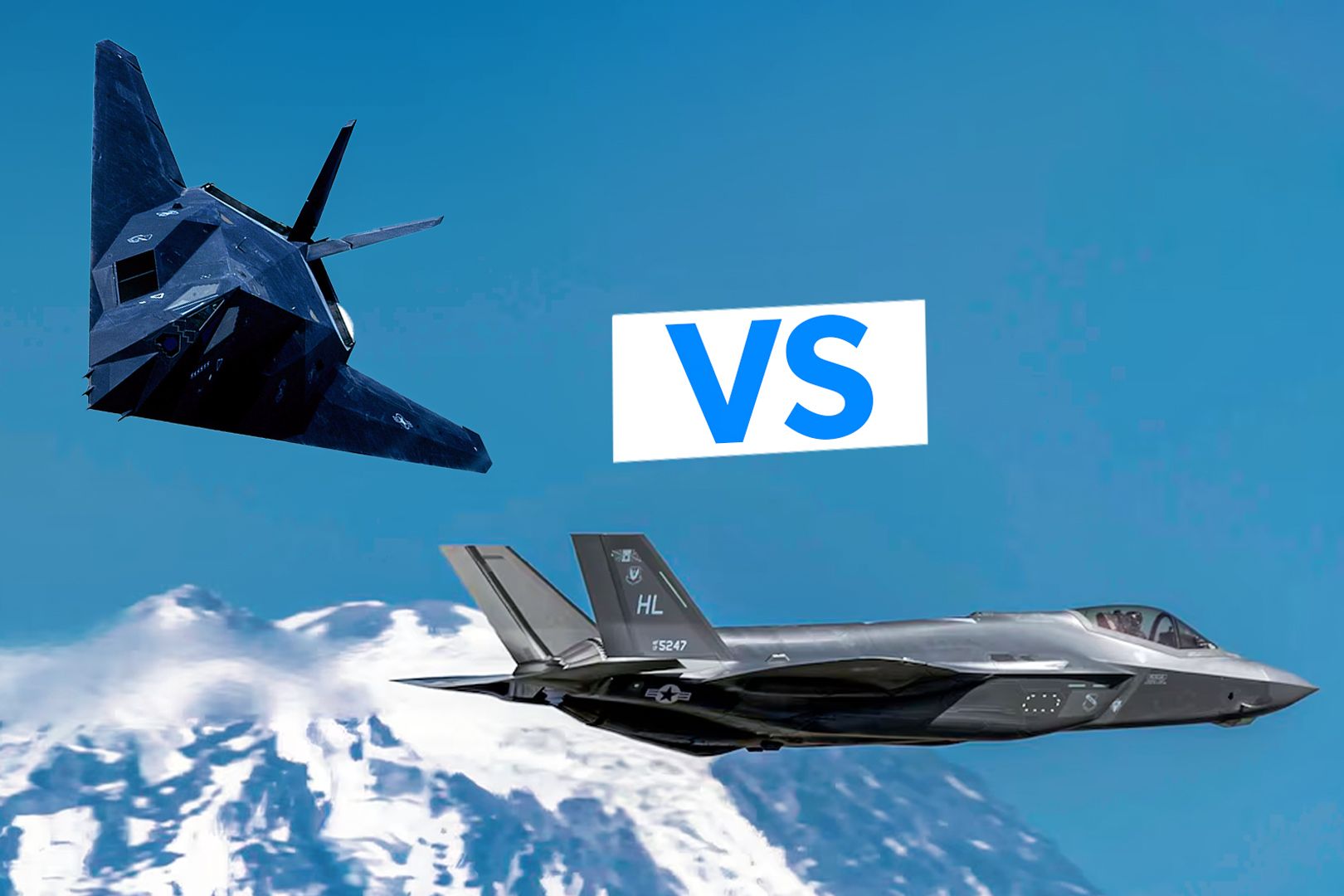
Summary The F-35 Lightning II, a powerful modern stealth combat aircraft, surpasses the F-117 Nighthawk in technology advancements. The F-117 Nighthawk, the first operational stealth aircraft, set the foundation for modern stealth technology with faceted design. The F-35 Lightning II employs superior stealth methods like radar-absorbent materials and IR suppression to enhance its capabilities.
Lockheed Martin has been involved in stealth technology research since the 1970s. In the late 1970s, what would become the world's first operational aircraft with stealth technology, the F-117 Nighthawk, was developed in response to the urgent need for a fighter aircraft that could fly undetected. Introduced in 1983, the single-seat subsonic F-117 took part in several wars and other critical historical events.

Lockheed Martin's stealth technology has significantly advanced in recent decades, introducing the most modern stealth multi-role combat aircraft, the F-35 Lightning Il, in 2015. While there still are a handful of F-117 Nighthawks in training service, there is no looking back on the F-35's exceptional intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. This article explores some similarities and differences between the two aircraft while noting how the F-117 paved the way for the future of stealth technology.
Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk Length : 65 ft 11 in (20.09 m) Wingspan : 43 f4 in (13.21 m) Height : 12 ft 5 in (3.
78 m) Max takeoff weight : 52,500 I (23,814 kg) Maximum speed : Mach 0.92 (594 kn, 684 mph, 1,100 km/h) Range : 930 NM (1,070 mi, 1,720 km) Service ceiling : 45,000 ft (14,000 m) The Lockheed F-117 Nighthawk is a subsonic twin-engine stealth attack aircraft designed and developed by the secretive Skunk Works division of Lockheed in the late 1970s. The aircraft was designed for the United States Air Force (USAF) to primarily counter Soviet surface-to-air missiles (SAMs).
Following several designs and iterations, the company proceeded with the F-117 development program in 1978. The aircraft performed its first flight in 1981, and the first production aircraft was delivered in 1982. However, the operations were kept secret not until 1990, when the aircraft made its first public appearance.
According to Lockheed Martin , “The aircraft achieved initial operational capability in 1983 but was kept under the strictest of secrecy for many years. It wasn't until 1988 that the program was publicly acknowledged, and not until 1990 that it made its first formal public appearance. By this time, the aircraft had been operational for seven years.
” Despite "smooth and blended" designs that are generally considered ideal for speed and stealth, an unconventional design and engine configuration were selected to achieve the unimaginable. The F-117's faceted-angle surfaces not only significantly reduced the radar signature but also helped deceive radar beams and subsequent algorithms. The necessary aerodynamic control was compensated for using a variety of computer systems.
The aircraft is powered by two General Electric F404 non-afterburning turbofan engines, each producing 9,040 lf (40.2 KN) thrust. The highly modified engines feature cooler operating temperatures resembling a turbojet functionality to aid the aircraft's stealth capabilities.
The conductive metal mesh grill in the engine intake obscured the engine from the radar. The thermal signature, generally identified from the engine exhaust, was significantly lowered by intentionally mixing cold air. A look at how stealthy the F-117A Nighthawk truly is.
Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II Length : 51.4 ft (15.7 m) Wingspan : 35 ft (11 m) Height : 14.
4 R. (4.4 m) Max takeoff weight : 65,918 lb (29,900 kg) Maximum speed : Mach 1.
6 at high altitude Range : 1,500 NM (1,700 mi, 2,800 km) Combat range : 760 NM (870 mi; 1,410 km), air-to-air configuration on internal fuel 4727 Service ceiling : 50,000 ft (15,000 m) The F-35 Lightning Il is the first operational supersonic short/vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) stealth fighter designed for air superiority and strike missions as part of the Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) program. The F-35 signifies a leap in stealth technology, particularly in terms of specialized materials and noise compression. The aircraft features a minimized radar cross-section (RCS) due to the specialized shaping of the airframe and the use of specialized materials.
The airframe is designed with continuous surface curvature and appropriate edge alignment. Moreover, the serration of skin panels masked with radar-absorbent materials enables a greater stealth capability compared to other aircraft. According to Lockheed Martin , “Integrating JASSM, LRASM and new technologies onto the F-35 suite continues to increase multi-role mission capabilities - helping to continue to make the F-35 the most lethal, stealthy and survivable aircraft in the world.
” Yes, another head-to-head matchup (on paper) for the F-35. This time, we compare it to the Rafale. With the aircraft's supersonic flight characteristics, it can produce large noise signatures.
The supersonic inlet uses a diverterless compression bump to divert the boundary layer away from the inlet duct, further reducing the aircraft's radar signature. While the airframe design and inlet characteristics evolved from F-117's stealth technology, the highly durable radar-absorbent fibermat skin is derived from earlier stealth aircraft, including the F-22 Raptor. The precise control of radio frequency control onboard the F-35 Lightning I reduces its infrared and visual signatures, preventing detection in the air.
With a design focus on high-frequency signals, using Luneburg lens reflectors further disguises the F-35 in the air. Stealth and electronic warfare (EW) are not mutually exclusive. But which one truly gives the edge to modern warbirds?.