Brown fat is associated with weight loss and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Exposure to somewhat cooler temperatures and eating certain foods, such as red pepper, may activate it. In contrast, some practices that boost brown fat may cause harm.
For instance, the keto diet, a popular eating plan with Weight Watchers, may not be a long-term healthy way of tapping into the potential benefits. Clinical dietitian Ria Hawle, who specializes in diabetes and cardiac nutrition, explained the difference between white and brown fat to The Epoch Times in an email. “Brown fat, located around the neck and above the collar bone, is a unique type of fat that is different from the more familiar white fat,” she said.
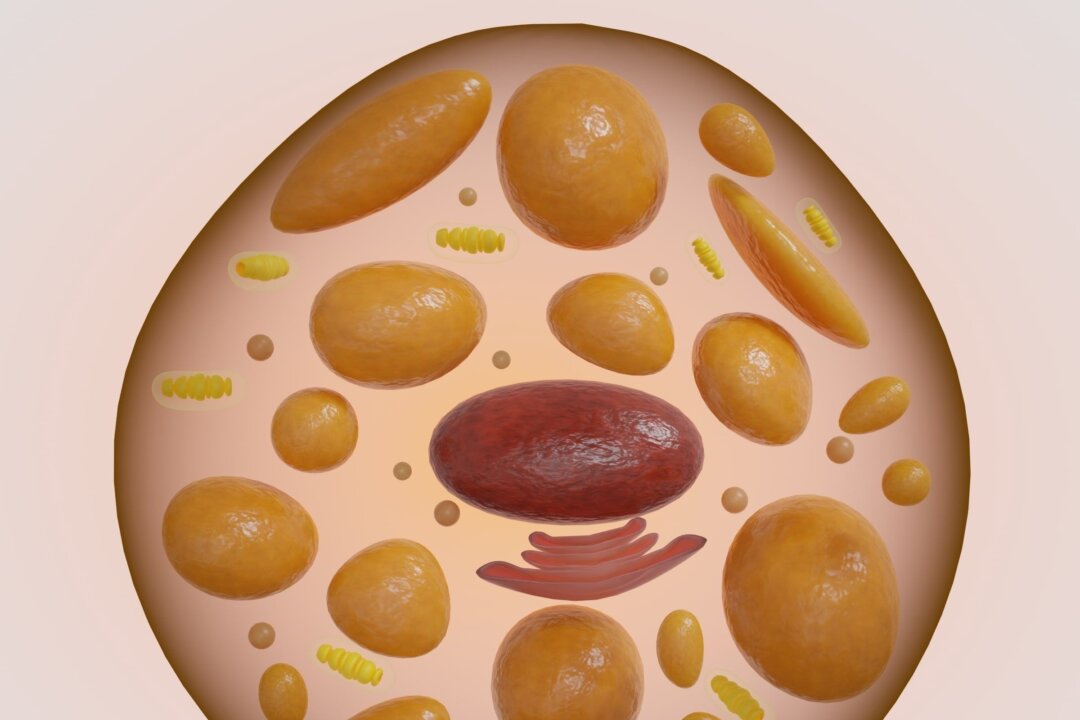
“White fat is all about storing energy, but brown fat burns calories. This burning happens through a process called thermogenesis, which involves heat generation through a high concentration of mitochondria, often called the powerhouses of the cells.” Type 2 diabetes Coronary heart disease Unhealthy blood lipids Cerebrovascular disease, conditions involving the blood flow to the brain High blood pressure Congestive heart failure A factor that may underlie the above benefits is that brown fat is connected to healthier white fat distribution, noted the CRM study.
This means it causes less white fat to be stored in the belly. When belly fat decreases, the risks associated with it also decline. “Most mitochondria in the body produce ATP, which is a un.